Filter
-
(1)
-
(1)
-
-
(1)
-
(1)
-
-
(16)
-
(1)
-
(1)
-
(1)
-
-
(3)
-
(2)
-
(1)
-
-
(2)
-
(1)
-
(1)
-
-
(27)
-
(9)
-
(11)
-
(12)
-
(10)
-
-
(1)
-
(1)
-
-
(4)
-
(4)
-
(1)
-
-
(7)
-
(7)
-
-
(3)
-
(5)
-
(1)
-
(1)
-
(1)
-
(1)
-
(1)
-
-
(47)
-
(25)
-
(1)
-
(1)
-
(2)
-
(1)
-
(2)
-
(16)
-
(4)
-
(8)
-
-
(13)
-
(6)
-
(4)
-
(2)
-
(2)
-
-
(6)
-
(2)
-
(2)
-
(1)
-
(1)
-
-
(2)
-
(1)
-
(1)
-
-
(16)
-
(7)
-
(2)
-
(9)
-
-
(1)
-
(1)
-
-
(2)
-
(2)
-
-
(4)
-
(4)
-
-
(2)
-
(5)
-
(4)
-
(1)
-
-
(4)
-
(2)
-
(2)
-
(1)
-
(1)
-
(1)
-
-
(2)
-
(1)
-
(1)
-
(1)
-
-
(20)
-
(6)
-
(9)
-
(8)
-
(4)
-
(1)
-
-
(3)
-
(1)
-
-
(3)
-
(1)
-
(1)
-
(3)
-
(1)
-
(1)
-
(1)
-
(1)
-
(1)
-
(1)
-
-
(3)
-
(1)
-
(1)
-
(2)
-
-
(49)
-
(2)
-
(10)
-
(7)
-
(15)
-
(12)
-
(1)
-
(1)
-
(4)
-
(1)
-
(5)
-
(2)
-
(4)
-
(5)
-
(1)
-
-
(6)
-
(1)
-
(1)
-
(1)
-
(1)
-
(1)
-
(1)
-
(1)
-
-
(51)
-
(1)
-
(3)
-
(2)
-
(9)
-
(1)
-
(5)
-
(1)
-
(20)
-
(8)
-
(7)
-
(1)
-
(10)
-
(2)
-
(1)
-
(2)
-
(1)
-
(1)
-
(1)
-
(1)
-
(9)
-
(5)
-
(1)
-
(9)
-
(6)
-
(58)
11 - 20 of 74 results
-
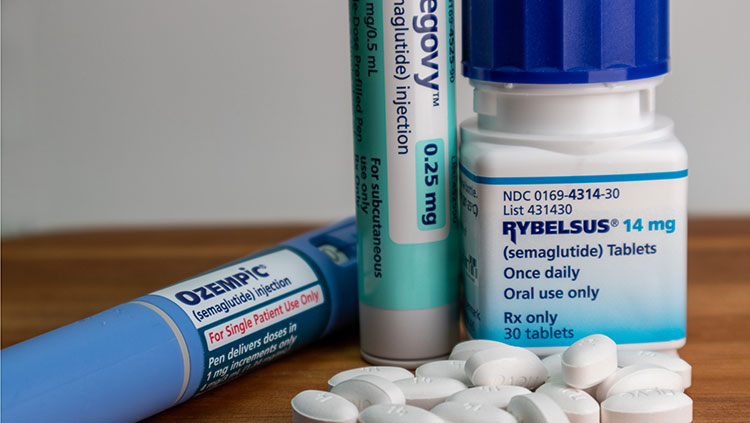
Researchers are examining whether drugs currently approved to treat obesity and type 2 diabetes could be useful for a wider range of health challenges.
-
Kay Tye studies the neuroscience behind social isolation and searches for new targets for mental health treatments that could address its impact.
-
Immune cells throughout the brain and body influence the processing of fear and anxiety, and their dysfunction may underly mental health disorders.
-
The blood-brain barrier protects your brain by ensuring the important things stay in while pathogens stay out.
-
NIH leaders from various institutes discussed the need to consider more social determinants of health in addiction research.
-
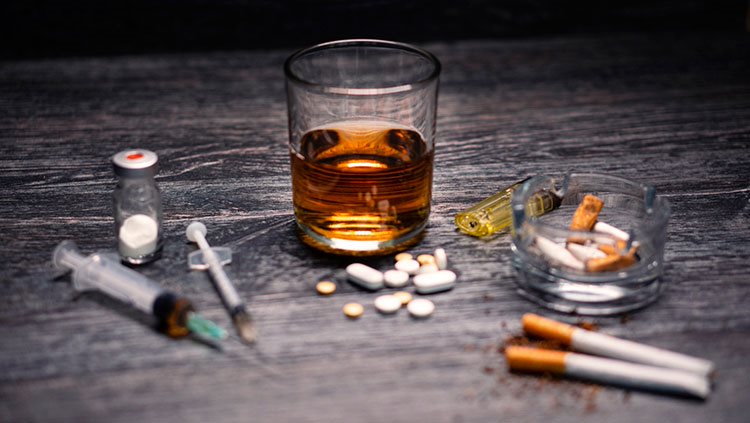
Smoking nicotine and drinking alcohol are common risk factors that can lead to premature death. Learn how both substances impact our bodies and can lead to addiction.
-
Drug abuse is one of the nation's most serious health problems. About 9 percent of Americans, more than 22 million people, abuse drugs on a regular basis. Drug abuse, including alcohol and nicotine, is estimated to cost the U.S. more than $600 billion each year.
-
And other neuroscience news you may have missed in November.
-
Moderate amounts of alcohol do not kill brain cells.
-
Opioids are substances that bind to opioid receptors in the brain to relieve pain.