ICYMI: Octopuses Change Colors During REM-Like Sleep
- Published9 Apr 2021
- Author Alexis Wnuk
- Source BrainFacts/SfN
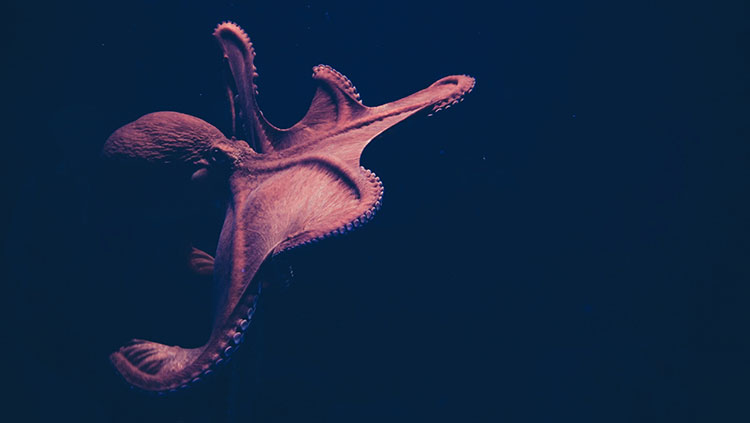

Octopuses Change Colors During REM-Like Sleep
Like humans, octopuses cycle through different stages of sleep, researchers reported March 25 in iScience. They collected four octopuses from the wild and housed them temporarily in the lab to watch them sleep. The octopuses spent most of their time in a quiet sleep stage, their bodies immobile and their skin pale. But every 30 minutes or so, they entered a twitchy stage of sleep where colors flickered across their skin. The researchers likened this stage to human REM sleep — a phase marked by rapid eye movements where most dreaming occurs — but it’s unclear if octopuses dream.
Related: Octopuses on MDMA Hint at the Evolution of Social Behavior
Read more: Octopus sleep includes a frenzied, colorful, ‘active’ stage. Science News
More Top Stories
- Scientists who unraveled the biology of migraine win Brain Prize. The Guardian
- Some COVID-19 long-haulers develop tinnitus. The New York Times
- Cuttlefish show remarkable self-control in a modified “marshmallow test.” NPR
- Neanderthals’ inner ear anatomy suggests they could perceive speech. Scientific American
- Young, critically endangered songbirds aren’t learning courtship songs — which could spell disaster for the species. The New York Times
- Mini-brains reveal the gene that helps humans grow big brains. New Scientist
- Tree frog lungs act like noise-cancelling headphones, muffling sounds of other animals. The Atlantic
- Smartphone addiction linked to poor sleep. The Guardian
- Virtual schooling may hurt kids’ — and parents’ — mental health. CNN
- After death, some brain cells may become more active. The Washington Post
- A protein in tooth cells detects pain from cold temperatures. The New York Times
- Jotting notes by hand is better for memory than typing. Fast Company
- Scientists implanted false memories in people — then reversed them. Vice
- Gene-silencing drug dampens pain in mice. Science
- Compounds in oily skin secretions could serve as biomarkers for Parkinson’s disease. Chemical & Engineering News
- Kids who spend more time in front of screens are more likely to develop binge-eating disorders. CNN
- Ancient memory trick improves memory and rewires the brain. Gizmodo
- Scientists read monkeys’ minds with ultrasound. Science
- People prone to feeling bored are more likely to ignore social distancing guidelines during the pandemic. Science News
- The cerebellum may play a role in alcohol metabolism. The Scientist
- Brisk walking improves thinking skills in older adults with early signs of memory loss. The New York Times
- Fingerprint ridges may aid the sense of touch. New Scientist
- Brain scans can predict how stocks will perform. The Guardian
CONTENT PROVIDED BY
BrainFacts/SfN
Also In Neuroscience in the News
Trending
Popular articles on BrainFacts.org