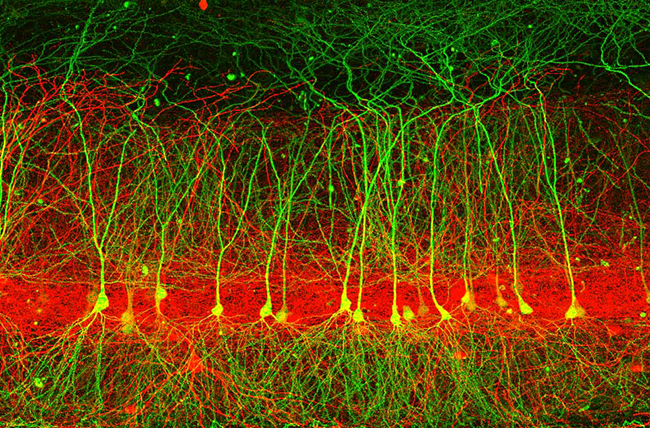
The key to understanding how our brains work lies in determining how each nerve cell or neuron continuously integrates the information it receives from other neurons via connections called synapses. For example, each pyramidal neuron (colored green) can receive tens of thousands of synapses from neurons belonging to several different brain regions. Interneurons (colored red) form local connections onto pyramidal neurons to form specific microcircuits. By using a combination of approaches including electrophysiology, microscopy, molecular biology and computer modeling, scientists are able to approach the complex puzzle of understanding how the 86 billion neurons in our brains make us who we are.
CONTENT PROVIDED BY

BioInteractive
Also In Cells & Circuits
Trending
Popular articles on BrainFacts.org